The Point of Divergence of the Unternehmen Seelöwe-Timeline is April 24, 1940, when Adolf Hitler chokes to death on a bite of apple in the Kehlsteinhaus. As a result, Deputy Führer Rudolf Hess is appointed Führer on May 5, 1940. All events preceding Hitler's death are the same as OTL, so I won't bother listing the events of WWII previous.
This is a List of Events in the Unternehmen Seeloewe Universe.
A New Führer[]
- April 24, 1940: Hitler chokes on an underchewed bite of apple and stops breathing in the Kehlsteinhaus. Despite Eva Braun's persistent CPR, he dies on the floor of his dining room. Senior members of the Nazi Party are alerted.

The isolated location of Kehlsteinhaus (visible at the top of the mountain) made it impossible for the Führer to get the medical attention that could have saved him.
- April 25, 1940: The public learns of the Führer's death when a distraught SS soldier, who witnessed the event, leaks the news to the press. A National Day of Mourning is quickly declared by Goebbels.
- April 26, 1940: Rudolf Hess is shot at, but not hit, as he leaves his office in Berlin by a young man, claiming to be a Polish national when captured by police.
- April 28, 1940: The Polish assassin finally admits that he was hired by Herman Göring to take out Hess. An SS search of Göring's apartment reveals damning evidence; Göring is arrested by the SS as he leaves a Berlin restaurant around 8 PM.
- May 5, 1940: Rudolf Hess is appointed Führer in Berlin.
The Nazi Conquest of Britain[]
- May 7, 1940: Hess orders the Wehrmacht to follow through with Hitler's plans to invade France several days early.
- June 4, 1940: Accelerated under Hess' command, the Luftwaffe begins bombing RAF bases in England, sparking the Battle of Britain.
- June 5, 1940: France surrenders, cementing Hess' popularity among the German people.
- June 21, 1940: The Norwegian Campaign of the War is completed, securing Sweden's supplies for Germany.
- June 22, 1940: In the Pacific, Japan seizes Hong Kong from the British.
- June 24, 1940: Hess is alerted of Hitler's plans to invade the Soviet Union on the twenty-fifth and, at the urging of the Wehrmacht generals, frantically recalls the forces deployed to invade.
- July 14, 1940: Nazi Germany signs the Neutrality Acts with the United States, popular among both the German and American public.
- July 24, 1940: President Roosevelt in America unwillingly accepts Nazi Germany into the binds of the Lend-Lease Acts. The American economy booms as production speeds up to fill the demands of both the British and the Germans.
- August 2, 1940: Frustrated with the slow process of the Battle of Britain, Hess orders Göring to begin targeting RAF fields and aircraft factories.
- August 10, 1940: Hess meets with Stalin in Warsaw. They sign the Warsaw Treaty of 1940 and reaffirm the fragile alliance between the two nations.
- September 17, 1940: Having successfully subdued the RAF, Nazi forces land on Britain's south coast.
- October 1, 1940: Nazi troops reach London. The Royal Family is evacuated to Scotland.
- October 13, 1940: Churchill is captured by German Army soldiers in Oxford as he attempts to evacuate to Scotland. Hess orders him to be sent to Berlin as a political prisoner.
- November 1, 1940: The British surrender at Edinburgh. A triumphant Hess places Britain under the rule of the British Union of Fascists and grants Ireland symbolic independence from Britain (Ireland remains a Nazi puppet regime, as does Britain).

The Flash and Circle Flag replaced the traditional Union Jack as the National Flag of Britain during the Nazi Occupation.
- November 5, 1940: The missing Royal Family of Britain appear in Toronto, having fled across the Atlantic on Halloween Night.
Lebensraum[]
- December 4, 1940: Following Hitler's plans (postponed for the British Invasion), Hess has the Wehrmacht engage Operation Maximilian, the invasion of the Soviet Union.
- January 12, 1941: Neutral United States issues a warning to Japan that engaging British or Australian warships within American territorial waters in the Pacific will be considered an act of war.
- January 15, 1941: Egypt falls to the Germans. Germany establishes the colonies of Nordägypten and Sueskanal out of the northern halve of British Egypt; Italy seizes southern Egypt and colonizes it as Sud Egitto.
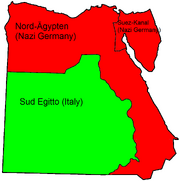
The Division of Occupied Egypt.
- April 9, 1941: The Japanese invade British Burma.
- April 10-27, 1941: German and Soviet forces battle over Smolensk and Stalingrad. Smolensk falls on the 22nd; Stalingrad falls five days later.
- July 4, 1941: Leningrad falls. The survivors of the Siege of Leningrad are shot execution-style by the SS. It is estimated fewer than three hundred Leningrad civilians survive the massacres.
- August 22, 1941: Moscow falls. Key members of the Communist Party are captured or killed; Stalin escapes and joins the rallying Red Army at Novosibirsk.
- December 1, 1941: British Burma falls to Japan.
- January 14, 1942: German and Italian forces surround Novosibirsk. The Red Army desperately attempts to repel the attack.
- May 2, 1942: Novosibirsk falls. Stalin is arrested, fleeing the city.
- May 10, 1942: Hess declares that the acquisition of German Lebensraum has been achieved; Nazi Germany now reaches from the Urals to France.
- May 11, 1942: Stalin is executed in Berlin. The Soviet Union is relegated to a rump state east of the Ural Mountains.
Peace in Europe[]
- April 1, 1943: Hess, after securing Europe for Nazi Control, begins dividing up conquered territories. His personal favorite is the German colonization of the old city of Leningrad, renaming it Neu Prußenstadt. He and senior Nazi Party officials begin planning the first of their Eastern European client states, Ostland.
- August 13, 1943: Winston Churchill is extradited to Canada. Prime Minister of Britain Oswald Mosley (under the dictation of Germany) allows the British Royal Family to return to Buckingham. King George refuses and vows to continue to fight Germany until his nation is liberated from German tyranny.
A Restless World[]
- August 4, 1944: British India declares independence after a Japanese-supported revolution.
- September 22, 1944: Japan and Australia call a truce.
- April 12, 1945: President Roosevelt dies. President Truman is inaugurated.
- June 17, 1945: Japan and China reach a truce agreement.
- August 29, 1945: Germany tests its first atomic bomb in the Arctic.

The German Pocket Battleship Graf Spee in the Arctic Ocean in front of the detonating Surtr atomic bomb
- December 5, 1945: Canada, the United States and the British government-in-exile sign the Vancouver Accords, cementing their support of one another. Germany and its allies condemn the Accords.
- March 23, 1946: The United States detonates her first atomic bomb in New Mexico.
- August 9, 1946: Japan tests her first atomic bomb in the South Pacific. Following their announcement, Canada declares that it's conducted over ten successful atomic tests in the Arctic.
- December 5, 1946: The USSR and China ally themselves to one another.
- May 5, 1947: The Philippines plunge into an anti-colonial war. The United States receives aid from Japanese guerrillas.
- June 8, 1947: The Union of the Americas is founded by the United States, Canada, and Brazil. Headquartered in New York, the UoA binds the nations together for military and economic support. Nazi Germany condemns the action.
- July 4, 1947: Rudolf Hess visits Washington, DC, and enjoys the Independence Day celebrations with President Truman. Despite persistently badgering Truman to revoke the United States' involvement with the UoA, Truman adamantly refuses.
- August 19, 1947: Mexico joins the UoA.
- November 10, 1947: Fascist Britain and the British government-in-exile, backed respectively by Nazi Germany and the UoA, begin fighting the Bermuda War, over the contested Bermuda Islands in the Atlantic.
- January 8, 1948: Nazi Germany gives the Ukraine independence as a puppet state.
- January 19, 1948: Benito Mussolini is killed in a car accident.
- April 10, 1948: The Bermuda War ends in victory for the British government-in-exile.
- September 5, 1948: Japan and the United States sign the Pacific Governance Treaty.
- November 10, 1948: The Soviet Union launches a surprise attack on the United States in Alaska, landing at the town of Homer on the Cook Inlet. Japan and Canada join in the war on the American side.

A Soviet T-26 Tank outside of Homer, Alaska
- January 22, 1949: The Soviet Army reaches Anchorage, Alaska. Soviet Premier Georgy Malenkov issues a press release from the Soviet capital at Magadan claiming "partial victory" over "Nazi swine collaborators".
- January 31, 1949: The onset of dissidence in Britain triggers rioting in London. The Fascist Party responds by declaring martial law for the rest of the county; this accidentally triggers more London rioting, as well as riots in Glasgow, Liverpool, Edinburgh, and Devon.
- February 7, 1949: Hess withdraws support for Fascist Britain. Without the heavy Nazi presence in Britain, the Fascist Government quickly loses control over particularly rebellious regions, Scotland and northern England in particular.
Peace Crumbles[]
- March 1, 1949: Britain is divided between the Welsh Communist Party, the Scottish Freedom Corps and the British Union of Fascists. This date is formally recorded as the beginning of the Second English Civil War.

Riot Police in London repel angry mobs on March 1st, 1949.
- March 19, 1949: The Alaska War reaches a stalemate. The United States contemplates the use of nuclear weapons on the front.
- April 1, 1949: The Soviet Union issues an official warning to the United States (and indirectly to the Nazis) that use of nuclear weapons against Soviet targets would be met with nuclear reprisal.
- April 9, 1949: Soviet forces take Fairbanks, Alaska. Rudolf Hess meets with US President Thomas Dewey in Copenhagen; Dewey is more receptive to Hess' deals and discussions.
- June 12, 1949: The United States uses an atomic bomb on a rebel base outside of Manila, the Philippines. The intended shock-tactic to quell the expensive rebellion results in a sudden jump in dissidence and rebel sympathies. This is the first time an atomic weapon is used on any target as an act of war.

The atomic cloud rising from the Manila Bombing
- July 3, 1949: A Scottish Freedom Corps raiding party in Fascist-held territory comes upon one of Fascist Britain's 156 atomic weapons, lost in the chaos of the Civil War. They smuggle it back to the SFC Headquarters in Leith, Scotland.
- July 23, 1949: Soviet forces land simultaneously on Hokkaido and Hawaii. The Alaska War and the Philippine Anti-Colonial War merge as Communist rebellion in the Philippines begin to show evidence of heavy Soviet support.
- August 18, 1949: The Red Army halts at the Alaska Panhandle and offers surrender to the Americans. America refuses, even as they are pushed ever farther back.
- October 1, 1949: The Soviet forces in Hawaii are defeated.
- October 2, 1949: The Scottish Freedom Corps detonates the captured nuclear bomb, nicknamed 'William Wallace', or 'Willie' for short, in a truck, smuggled into London by Scottish commandos. Its intended target was the Smithfield neighborhood of London (the site of the historical figure and Scottish folk hero William Wallace's execution), however, detection and pursuit by Fascist security forces forced the SFC commandos to detonate the weapon in nearby Whitechapel. The act is condemned by Nazi Germany, the United States, the Soviet Union, Japan and the British government-in-exile. Winston Churchill was quoted as calling the act "despicable".
- January 1, 1950: The United States intervenes in Great Britain, sending some 4,000 troops to suppress violent rioting in the major cities. Surprisingly, Germany does not object - rather, they also intervene, sending another 5,000 SS troops to London.
- April 18, 1950: Soviet forces entrenched north of Juneau, Alaska send a Tu-4 bomber to drop a nuclear weapon on American forces in Juneau. An American anti-aircraft gun damages the bomber's right wing. As the aircraft plummeted towards American entrenchments, the bomb detonates in the rear, destroying the vanguard of the American forces.
- April 20, 1950: The United States, Nazi Germany and Japan launch an extreme reprisal against the Soviet Union for the April 18 Juneau Bombing. Primarily using German A-4 missiles, the three nations strike at over thirty Soviet cities, military bases and towns. The attacks kill tens of thousands of Soviets; sunsets globally are hazed with a bloody red hue from the smoke and dust of the explosions.
- April 21, 1950: The heavily weakened Soviets manage to fire their own reprisal weapon at the United States - the Tsar Bomba. The weapon annihilates much of Washington, DC, and is the largest nuclear weapon in history. President Dewey, his Vice President and the Speaker of the House are killed; the majority of the Senators and Congressmen, however, are not in the city, as Congress is not in session.
