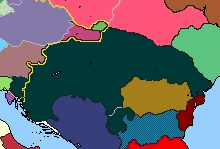
| |||||||
| Capital | Budapest | ||||||
| Largest city | Budapest | ||||||
| Language official |
Hungarian | ||||||
| others | Austrian and Greek | ||||||
| Demonym | Hungarians | ||||||
| Government | Democratic Monarchy | ||||||
| King | Olivér of Arpad | ||||||
| Population | 5,015,000 | ||||||
| Independence | 1000 | ||||||
| Currency | Forint | ||||||
The Kingdom of Hungary came into existence in Central Europe when Stephen I, Grand Prince of the Hungarians, was crowned king in 1000 or 1001. He reinforced central authority and forced his subjects to accept Christianity. Although all written sources emphasize only the role played by German and Italian knights and clerics in the process, a significant part of the Hungarian vocabulary for agriculture, religion and state was taken from Slavic languages. Civil wars and pagan uprisings, along with attempts by the Holy Roman Emperors to expand their authority over Hungary, jeopardized the new monarchy. The monarchy stabilized during the reigns of Ladislaus I (1077–1095) and Coloman (1095–1116). These rulers occupied Croatia and Dalmatia with the support of a part of the local population. Both realms retained their autonomous position. The successors of Ladislaus and Coloman—especially Béla II (1131–1141), Béla III (1176–1196), Andrew II (1205–1235), and Béla IV (1235–1270) — continued this policy of expansion toward the Balkan Peninsula and the lands east of the Carpathian Mountains, transforming their kingdom into one of the major powers of medieval Europe.
History[]
Our expansion goes well with a victory capturing Ragusa in 1503, then in 1504 we take over the capital city. The territory Ragusa is fulling incorporated into our nation as of 1505. A civil war breaks out in in the Transylvania county funded by the Wallachia in 1514. Our armies are able to stop them funding the rebels. We lose Transylvania and Moldova territories in 1515. In the same year the King creates a cabinet and court system in the government. Men over the age of 18 are allowed to vote for new judges, cabinet members and for each jury when a trail has to happen. The House of Commons was made this year in 1517. A House of Barons is made this year in 1518. The new anthem for the nation was made https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n-Dh3ftkRAs. As of 1524, most Jungist people are expelled from the nation except if they are in prison and then sent to Russia. We try to invade Slovakia in 1525 but after fighting nothing really happens between the two nations. After a second year battling Slovakia nothing really significant happens and both sides just lose men in the process. Our army invades Krakow to expand our borders and gain more land in the year 1534. After the invasion we win the war annexing Krakow. To help Byzantium in 1538 out we send our troops to northern Serbia to invade them. Since Byzantium didn't need our help a year later they give us land by the river in north Serbia. A small number of Unitarian Christians start their own communities along the borders of Poland and Bohemia. This new Christian religion is started by a guy named Stefan Baley. He brings the idea to many theologians and nobles. A few new churches are built for this new Christian religion. An invasion of Istria has taken place in the year 1544. We annex Istria into our nation after beating them. In the city of Zadar a large sea organ is made which plays music by way of sea waves and tubes located underneath a set of large marble steps. We invade Friuli-Venezia Giulia in the year 1550. We lost the war against Friuli Venezia Giulia. We invade Transylvania in 1553 to regain our old lands that were lost years ago in the civil war. We invade Transylvania in 1553 to retake our lands. Next year we try again after losing. After losing the first time in the second year fighting Transylvania we are able to push them back. The Byzantines intervene in our war but we resist them. As a result the battle is still contended. After 3 years of fighting we finally win and annex Transylvania. As an after result of the war general John Zápolya retires from the military at the age of 66.
Foreign Relations[]
Positive[]
- Russia
- Bohemia
- Saxony
- Poland
- Portugal
- Hesse
- Byzantium
Negative[]
Government[]
Feudalism[]
Was a combination of legal, economic, military and cultural customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships that were derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labor. Although it is derived from the Latin word feodum or feudum (fief), which was used during the Medieval period, the term feudalism and the system which it describes were not conceived of as a formal political system by the people who lived during the Middle Ages. With a set of reciprocal legal and military obligations which existed among the warrior nobility and revolved around the three key concepts of lords, vassals and fiefs. The head family/King is the ruler of such lands and nation. The House of Arpad is the leading family in the nation.
Cabinet[]
Members of a cabinet are usually called cabinet ministers or secretaries. The function of a cabinet varies: in some countries it is a collegiate decision-making body with collective responsibility, while in others it may function either as a purely advisory body or an assisting institution to a decision making head of state or head of government. Cabinets are typically the body responsible for the day-to-day management of the government and response to sudden events, whereas the legislative and judicial branches work in a measured pace, in sessions according to lengthy procedures. In our government, members of the Cabinet are given the title of Minister, and each holds a different portfolio of government duties ("Minister for the Environment", etc.). Every four years men over the age of 18 are allowed to vote for new members of the Cabinet.
Courts[]
A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law. In both common law and civil law legal systems, courts are the central means for dispute resolution, and it is generally understood that all people have an ability to bring their claims before a court. Similarly, the rights of those accused of a crime include the right to present a defense before a court. The system of courts that interprets and applies the law is collectively known as the judiciary. The place where a court sits is known as a venue. The room where court proceedings occur is known as a courtroom, and the building as a courthouse; court facilities range from simple and very small facilities in rural communities to large buildings in cities. The practical authority given to the court is known as its jurisdiction (Latin: jus dicere') – the court's power to decide certain kinds of questions or petitions put to it. a court is constituted by a minimum of three parties: the actor or plaintiff, who complains of an injury done; the reus or defendant, who is called upon to make satisfaction for it, and the judex or judicial power, which is to examine the truth of the fact, to determine the law arising upon that fact, and, if any injury appears to have been done, to ascertain and by its officers to apply a legal remedy. It is also usual in the superior courts to have barristers, and attorneys or counsel, as assistants, though, often, courts consist of additional barristers, bailiffs, reporters, and perhaps a jury. The term "the court" is also used to refer to the presiding officer or officials, usually one or more judges. The judge or panel of judges may also be collectively referred to as "the bench" (in contrast to attorneys and barristers, collectively referred to as "the bar"). Every ten years a new judge is appointed to server voted in by men over the age of 18. With the jury people they are voted in every trial by men over the age of 18.
House of Commons[]
The House of Commons is made up of each ruler of each county to discuss matters with the nation. It serve as the voice of the tax-paying subjects of the counties. In many cases, however, the council demanded the redress of the people's grievances before proceeding to vote on taxation. Thus, it developed legislative powers. Knights of the shire, elected from each county, were usually landowners, while the borough members were often from the merchant classes. These members represented subjects of the Crown who were not Lords Temporal or Spiritual, who themselves sat in the House of Barons. The House of Commons gained its name because it represented communities (communes). Members of the Commons elected a head of the Commons every five years to be the voice of reason to the King.
House of Barons[]
Membership is granted by appointment or else by heredity or official function. The membership of the House of Barons is drawn from the peerage and is made up of Lords Spiritual and Lords Temporal. While the House of Commons has a defined number of seats membership, the number of members in the House of Barons is not fixed. The House of Barons is the only upper house of any bicameral parliament in the world to be larger than its lower house. The House of Barons scrutinizes bills that have been approved by the House of Commons. It regularly reviews and amends Bills from the Commons. While it is unable to prevent Bills passing into law, except in certain limited circumstances, it can delay Bills and force the Commons to reconsider their decisions. In this capacity, the House of Barons acts as a check on the House of Commons that is independent from the electoral process. Bills can be introduced into either the House of Barons or the House of Commons. While members of the Barons may also take on roles as government ministers, high-ranking officials such as cabinet ministers are usually drawn from the Commons. The House of Barons has its own support services, separate from the Commons, including the House of Lords Library. People of the House of Barons elect their own head of the House every five years.
Military[]
Army[]
30,000 troops (black army)
[]
145 ships
Territories[]
- Banate of Bosnia
- Banate of Severin
Maps[]
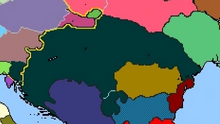
With Ragusa expansion
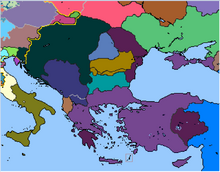
After our loss of lands in the civil war

With Krakow expansion
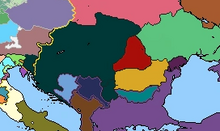
With land given to us from Byzantium
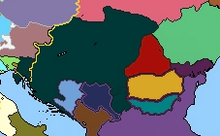
With Istria annexed
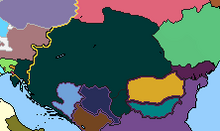
With Transylvania annexed back